In Flutter, handling asynchronous operations—like fetching data from an API or reading from a database—is a common task. The FutureBuilder widget is a powerful tool that allows you to build widgets based on the state of a Future. This tutorial walks you through how to use FutureBuilder effectively.
What is a FutureBuilder?
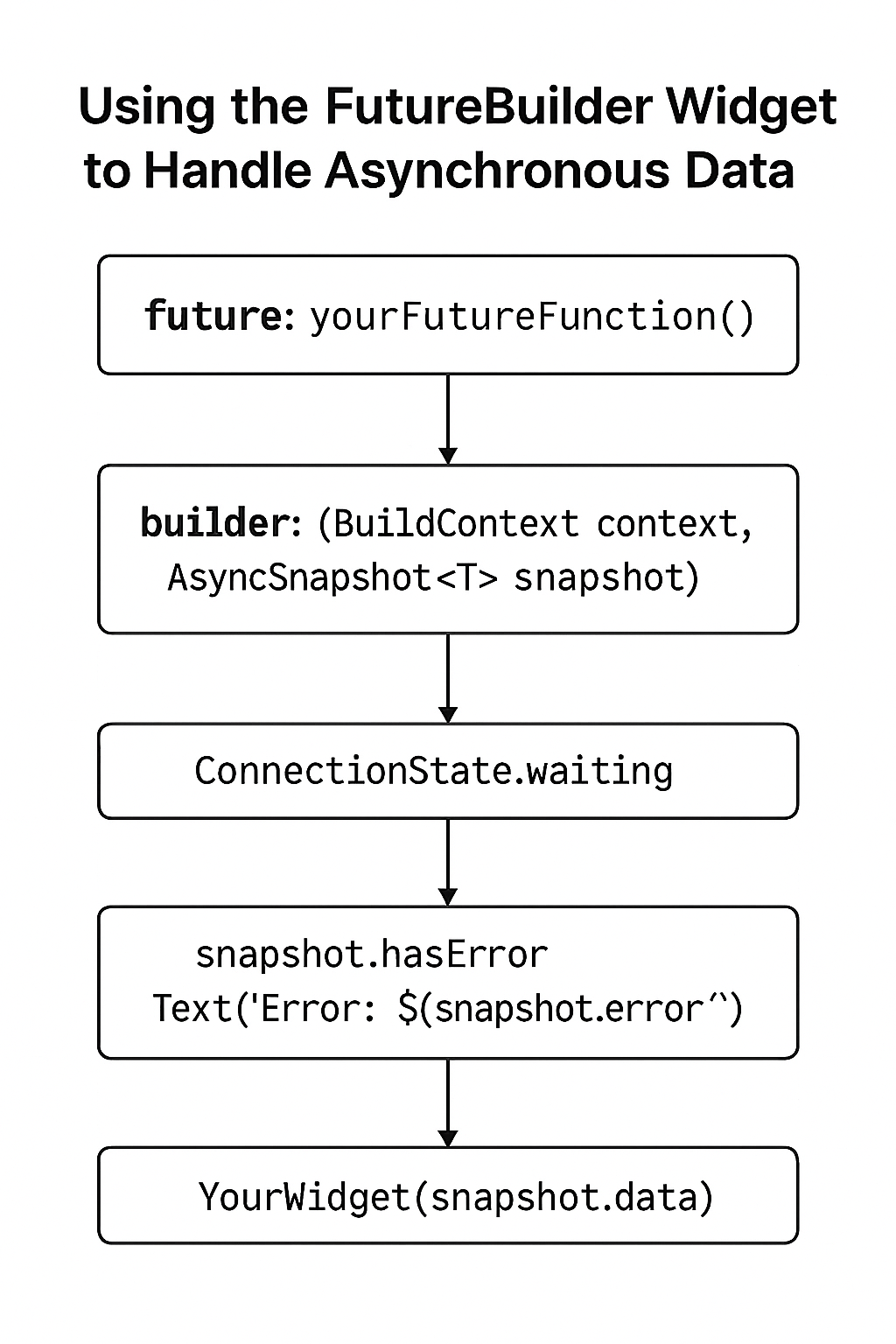
FutureBuilder is a widget that builds itself based on the latest snapshot of interaction with a Future. It listens to the Future and rebuilds its child widgets when the Future completes, fails, or is still loading.
Basic Structure
FutureBuilder<T>(
future: yourFutureFunction(),
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot<T> snapshot) {
if (snapshot.connectionState == ConnectionState.waiting) {
return CircularProgressIndicator();
} else if (snapshot.hasError) {
return Text('Error: ${snapshot.error}');
} else {
return YourWidget(snapshot.data);
}
},
)
Step-by-Step Example
Let’s build a simple app that fetches a list of posts from a placeholder API and displays them.
1. Define the Mode
class Post {
final int id;
final String title;
Post({required this.id, required this.title});
factory Post.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return Post(
id: json['id'],
title: json['title'],
);
}
}
2. Create the Fetch Function
</pre>
Future<List<Post>> fetchPosts() async {
final response = await http.get(Uri.parse('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts'));
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
List<dynamic> jsonData = json.decode(response.body);
return jsonData.map((item) => Post.fromJson(item)).toList();
} else {
throw Exception('Failed to load posts');
}
}
<pre>
3. Use FutureBuilder in the UI
class PostsPage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Posts')),
body: FutureBuilder<List<Post>>(
future: fetchPosts(),
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.connectionState == ConnectionState.waiting) {
return Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
} else if (snapshot.hasError) {
return Center(child: Text('Error: ${snapshot.error}'));
} else if (!snapshot.hasData || snapshot.data!.isEmpty) {
return Center(child: Text('No posts found.'));
} else {
return ListView.builder(
itemCount: snapshot.data!.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final post = snapshot.data![index];
return ListTile(
title: Text(post.title),
subtitle: Text('Post ID: ${post.id}'),
);
},
);
}
},
),
);
}
}
Best Practices
- Always handle all possible states: loading, error, and success.
- Avoid calling the
Futuredirectly inside thebuildermethod. Instead, pass it as a parameter toFutureBuilder. - Use caching or state management if the data should persist across rebuilds.
Conclusion
FutureBuilder simplifies the process of working with asynchronous data in Flutter. By understanding its lifecycle and properly handling its states, you can build responsive and robust UIs that react to data changes.